All Categories
Featured
2 people purchase joint annuities, which supply a guaranteed revenue stream for the rest of their lives. If an annuitant passes away during the distribution period, the remaining funds in the annuity might be passed on to a marked recipient. The certain alternatives and tax obligation effects will depend on the annuity agreement terms and relevant regulations. When an annuitant dies, the rate of interest earned on the annuity is taken care of in different ways depending upon the sort of annuity. For the most part, with a fixed-period or joint-survivor annuity, the passion continues to be paid out to the making it through recipients. A survivor benefit is a function that makes sure a payout to the annuitant's recipient if they die prior to the annuity repayments are tired. Nevertheless, the availability and terms of the survivor benefit may vary depending upon the particular annuity contract. A sort of annuity that quits all repayments upon the annuitant's fatality is a life-only annuity. Recognizing the conditions of the survivor benefit before purchasing a variable annuity. Annuities undergo taxes upon the annuitant's fatality. The tax obligation treatment relies on whether the annuity is held in a qualified or non-qualified account. The funds undergo income tax obligation in a certified account, such as a 401(k )or individual retirement account. Inheritance of a nonqualified annuity commonly leads to taxes only on the gains, not the entire quantity.
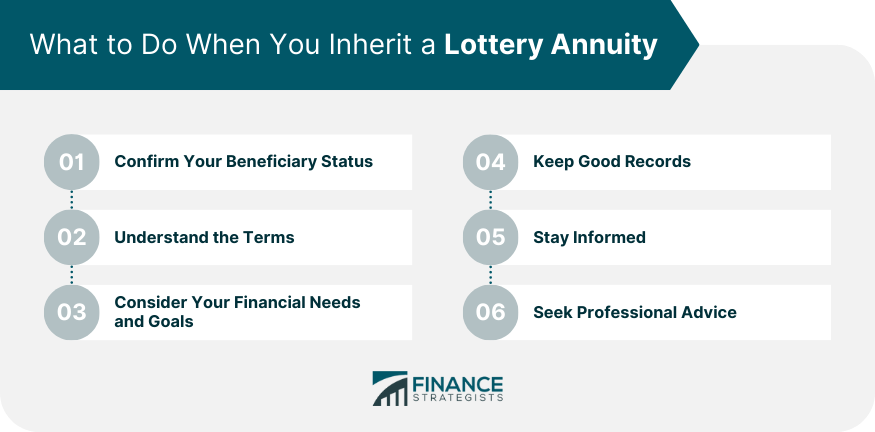
The original principal(the quantity at first deposited by the moms and dads )has actually currently been tired, so it's exempt to tax obligations once again upon inheritance. The earnings section of the annuity the passion or investment gains accrued over time is subject to earnings tax. Typically, non-qualified annuities do.
have died, the annuity's advantages commonly return to the annuity owner's estate. An annuity proprietor is not legally needed to notify existing beneficiaries regarding adjustments to recipient designations. The choice to alter beneficiaries is generally at the annuity owner's discernment and can be made without informing the existing recipients. Because an estate technically doesn't exist until an individual has actually died, this recipient designation would just enter effect upon the fatality of the called person. Usually, once an annuity's proprietor passes away, the designated recipient at the time of death is entitled to the benefits. The spouse can not alter the recipient after the proprietor's fatality, even if the beneficiary is a minor. However, there might specify stipulations for taking care of the funds for a small recipient. This typically entails assigning a guardian or trustee to take care of the funds until the kid gets to adulthood. Normally, no, as the beneficiaries are not responsible for your financial obligations. It is best to consult a tax obligation specialist for a details response associated to your case. You will remain to obtain payments according to the agreement timetable, but trying to get a round figure or lending is likely not an alternative. Yes, in nearly all cases, annuities can be inherited. The exemption is if an annuity is structured with a life-only payment choice through annuitization. This type of payment stops upon the fatality of the annuitant and does not supply any kind of recurring value to beneficiaries. Yes, life insurance policy annuities are generally taxed
When taken out, the annuity's profits are exhausted as average income. Nonetheless, the primary quantity (the preliminary financial investment)is not taxed. If a recipient is not named for annuity benefits, the annuity continues normally go to the annuitant's estate. The distribution will certainly adhere to the probate procedure, which can postpone settlements and may have tax implications. Yes, you can call a count on as the beneficiary of an annuity.
Is there tax on inherited Annuity Rates

Whatever section of the annuity's principal was not already taxed and any type of revenues the annuity accumulated are taxable as income for the beneficiary. If you inherit a non-qualified annuity, you will only owe taxes on the earnings of the annuity, not the principal utilized to acquire it. Since you're getting the whole annuity at once, you should pay taxes on the whole annuity in that tax obligation year.
Latest Posts
Exploring the Basics of Retirement Options A Comprehensive Guide to Investment Choices Breaking Down the Basics of Investment Plans Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Retirement Plans Why Choos
Decoding How Investment Plans Work A Comprehensive Guide to Indexed Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Defining the Right Financial Strategy Pros and Cons of Tax Benefits Of Fixed Vs Variable Annuities Why Choo
Analyzing Strategic Retirement Planning A Comprehensive Guide to Fixed Income Annuity Vs Variable Annuity What Is the Best Retirement Option? Benefits of Choosing the Right Financial Plan Why Choosing
More
Latest Posts